Internal Medicine 2018
About the Conference
The EuroSciCon is holding its 7th European Congress on Internal Medicine & Patient Care (Internal Medicine-2018) from March 26-27, 2018, Vienna, Austria. The theme of this meeting is "Internal Medicine: A New System for Patient Care " which will provide an international platform to discuss the present and future challenges in primary care, patient care, continuing education and expertise meeting. Internal Medicine conferences aim to promote continuous medical education and encourage a nourishing exchange of facts and ideas in how to deal with the disorders involving patients. Great scientific faculty from USA, Europe as wel as other continents expect a highly interesting scientific as wel as representative event.

Internal Medicine Conference Highlights & Benefits:
SCOPE of Internal Medicine- 2018:
It estimated that, most of the countries have an absolute shortage of 2.3 million physicians and nurses. These shortages of primary health care professionals, suggest that many countries have insufficient numbers of health professionals to deliver essential health interventions. Shortage is defined as having a projected supply of primary physicians that meets less than 80% of the forecasted primary care demand at estimated means.
A Primary care physician is our main health care provider in non-emergency situations. Doctors, who have completed a residency in internal medicine, are board-certified, in primary care specialty. The scope of their practice includes the care of all ages for different medical problems. They provide preventive care and teach healthy lifestyle choices. They identify and treat common medical conditions, and helps the patients in avoiding many non-communicable diseases such as heart disease, stroke, cancer, chronic respiratory diseases and diabetes, which are the leading cause of mortality in the world.
WHO should attend Internal Medicine-2018:
Internal medicine-2018 welcomes experts from both academia and industries.
Experts such as Deans/Chairs, Vice Deans & Vice Presidents of Medical Institutions and Hospitals working in the field of Internal Medicine and related discipline, but not limited to:
- Emergency Medicine
- Intensive Care Medicine
- Adult Diseases
- Primary Care
- Geriatrics
- Patient Care
- Telemedicine
- Healthcare
- Oncology
- Genomic Medicine
Professors and students from academia who are in the field of Medical and clinical research.
Physicians, Business delegates, Directors / Managers & Business Intelligence Experts, Departmental Managers.
About Venue
Vienna is the capital and largest city of Austria . Vienna is Austria's primary city, with a population of about 1.8 million, and its cultural, economic, and political center. It is the 7th-largest city by population within city limits in the European Union. It has the second largest number of German speakers after Berlin. Vienna is host to many major international organizations, which includes United Nations and OPEC. The city is located in the eastern part of Austria and is close to the borders of the Czech Republic, Slovakia, and Hungary. These regions work together in a European Centrope border region. Along with nearby Bratislava, Vienna forms a metropolitan region with 3 million inhabitants. In 2001, the city center was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Scientific Sessions & Tracks
Illnesses that affect the adults are recognized by internist during diagnosis and treatment, prevention of general or chronic disease conditions cover under internal medicine and patient care. All the general, rare diseases, severe chronic illnesses are covered under this session.
Track 1: Internal Medicine & Patient Care:
Internal medicine is the medicinal characteristic dealing with the prevention, detections and treatment of adult diseases. Physicians specializing in internal medicine are called internists, or in Commonwealth nations. Internists are experienced in the management of patients who have multi-system disease processes. Internal medicine patients are often seriously diseased or require complex examination; internists do much of their work in hospitals. Internists often have subspecialty interests in disorder affecting particular organs or organ systems. Patient care is defined as the management of hospital facilities, assistance and staff as per the therapeutic and nursing needs of the patient. Internists care for confined and ambulatory patients and may play an extensive aspect in teaching and research.
Primary care is the routine healthcare given by a health care server. Typically this provider acts as the first contact and leading point of advancing care for patients within a healthcare system and organizes other specialist care that the patient may need. Patients generally receive primary care from specialist such as a primary care physician, an adult-gerontology nurse practitioner, Pediatric nurse practitioner and family nurse practitioner or a physician assistant. Depending on the nature of the health condition, patients may then be referred for secondary or tertiary care.
Intensive care medicine is a branch of medicine board with the diagnosis and administration of life-threatening disease cases requiring organ support and invasive auditing. Patients requiring intensive care may compel support for instability, acute renal failure, respiratory compromise, lethal cardiac arrhythmias or the increasing effects of multiple organ failure, more frequently referred to now as multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. They may also be introduced for invasive auditing, such like the crucial hours after major surgery when allow too unstable to transfer to a less intensively auditor unit. Intensive care is usually only offered to those whose condition is potentially reversible and who have a good chance of surviving with intensive care support. A prime requirement for admission to an intensive care unit (ICU) is that the underlying case can be defeated. Critical care medicine is a relatively new but increasingly important medical specialty. Physicians with training in critical care medicine are referred to as intensivists.
Infectious diseases are disorder caused by micro-organisms such as viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi, these diseases can be spread, directly or indirectly, from one person to another. They're normally harmless or even helpful, but under certain case, some organisms may source of disease. Infectious disease results from the coaction between those few microorganisms and the defences of the hosts they infect. However a host's immune system can also cause harm to the host itself in an attempt to control the infection.
Emergency medicine is the medical specialty involving care for identical and unscheduled patient’s volunteers with injuries requiring immediate medical treatment. Emergency physicians are responsible for beginning examinations and interventions to investigate and treat patients in the acute phase including initial rejuvenation and stabilization, coordinating care with doctors from other specialities, and making opinion regarding a patient's need for hospital admission, examination and discharge. Emergency physicians generally practice in hospital emergency departments, pre-hospital settings through emergency medical assistance and intensive care units.
An adult disease being that canappear, but are not usually studied in the pediatric and child population: Schatzki's ring, Helicobacter pylori, cricopharyngeal achalasia, pancreatic carcinoma, achalasia, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, adenocarcinoma of the colon, malignant melanoma, thyroid carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma, leiomyosarcoma of the ovary and sarcoidosis, hydatidiform mole. Radiologists explaining pediatric or child imaging should observe these entities and perform a proper diagnostic workup.
Epidemiology is the course and analysis of the patterns, source and effects of health and epidemic conditions in specified populations. It is the keystone of civic health and shapes management decisions and data-based practice by identifying exposure factors for disorder and mark for precautionary healthcare. Epidemiologist’s assisted with study method, selection, and statistical analysis of evidence; alter interpretation and propagation of results. Epidemiology has helped evolve technique used in clinical research, civic health course and to a lesser intensity, basic research in the biological system.
Geriatrics is a study that focuses on health care of aged people. It aims to stimulate health by countering and treating disorders and disabilities in elder adults. Geriatric physician who specialist in the care of older person. It is important to note the difference between geriatrics, the care of aged people, and gerontology, which is the study of the aging process itself. Geriatrics varies from standard adult medicine because it targeted on the particular needs of the aged person. The aged body is various physiologically from the younger developed body and during old age.
Telemedicine is the study of an information technology and telecommunication to contribute clinical health care from a span. It has been used to taken distance boundaries and to better access to medical assistance that would generally not be frequently available in remote rural communities. It is also used to save lives in critical care and emergency situations. These technologies consent communications between patient and medical agent with both convenience and devotion, as well as the communication of medical, design and health services evidence data from one site to another.
Sports medicine is a study of medicine that deals with physical fitness and the treatment and prevention of fractures related to games and exercise. Games and exercise medicine physicians are specialist doctors who have completed medical school, appropriate residency training and then specialize further in sports medicine. Specialization in sports medicine may be a doctor's first specialty. It may also be a sub-specialty following a specialization such as orthopedic surgery and psychiatry. The various approaches reflect the medical culture in different countries.
A chronic condition is a human health condition or disorder that is persistent or otherwise long-lasting in its effects or a disease that comes with time. The term chronic is often applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three months. In medicine, the opposite of chronic is acute. A chronic study is further distinguished from a recurrent course; recurrent diseases relapse continuously, with periods of remission in between. Chronic conditions have often been used to describe the various health related states of the human body such as syndromes, physical impairments, disabilities as well as diseases.
Diagnosis is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. Diagnosis is often challenging, because many signs and symptoms are nonspecific. Thus differential diagnosis, in which several possible explanations are compared and contrasted, must be performed. This involves the correlation of various pieces of information followed by the recognition and differentiation of patterns. Occasionally the process is made easy by a sign or symptom (or a group of several) that is pathognomonic. The information required for diagnosis is typically collected from a history and physical examination of the person seeking medical care. Often, one or more diagnostic procedures, such as diagnostic tests, are also done during the process. Sometimes Posthumous diagnosis is considered a kind of medical diagnosis.
Internal medicine and Healthcare:
Health care is the maintenance or improvement of health through the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in human beings. Healthcare is delivered by health professionals in allied health professions, chiropractic, physicians, dentistry, physician associates, midwifery and other health professions. It includes the work done in providing primary care, secondary care, and tertiary care, as well as in public health
Nephrology is a branch of medicine and pediatrics that concerns itself with the kidneys. It deals with the study of normal kidney function and kidney problems, the preservation of kidney health, and the treatment of kidney problems, from diet and medication to renal replacement therapy. Systemic conditions such as autoimmune disease and diabetes affect the kidneys and systemic problem such has hypertension occurs as a result of kidney problems are studied in nephrology.
Oncology is a branch of medicine dealing with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of cancer. The oncologist is a medical professional who practices oncology. There are three components which have improved survival in cancer:
- Prevention - This is by reduction of risk factors like tobacco and alcohol consumption.
- Early diagnosis - Screening of common cancers and comprehensive diagnosis and staging
- Treatment - Multimodality management by discussion in tumor board and treatment in a comprehensive cancer center.
Cancers are managed by attending multi-disciplinary cancer conferences where the surgical oncologist, pathologist, medical oncologist, organ specific oncologists meet to find possible management for individual patient considering the social, emotional, physical, psychological and financial status of patients.
Endocrinology is a branch of medicine and biology, which deals with the endocrine system and its diseases. It also deals with specific secretions known as hormones. Endocrinology specializations include comparative and behavioral endocrinology. It is also concerned with growth and development, sleep, tissue function, respiration, digestion, mood, stress, excretion, lactation, behavioral and psychological activities of metabolism, reproduction and sensory perception caused by hormones. Endocrinologists are frequently involved with the management and diagnosis of
- Hypothalamic disorders
- Gonadal disease
- Pituitary diseases
- Parathyroid abnormalities
- Lipid metabolism
- Iatrogenic effect of glucocorticoids
- Pancreatic endocrine disease
- Thyroid diseases Adrenal cortex dysfunction
Genomics is the study of genomes, the complete set of DNA within a cell of an organism. More specifically, genomics involves the sequencing and analysis of genomes. Genomics is also concerned with the structure, function, evolution, and mapping of genomes. In contrast to genetics, which refers to the study of individual genes and their roles in inheritance, genomics uses high DNA sequencing and bioinformatics to assemble, and analyze the function and structure of entire genomes. The field also includes studies of intragenomic phenomena such as heterosis , epistasis , pleiotropy and other interactions between loci and alleles within the genome. Advances in genomics have triggered a revolution in systems biology which facilitates the understanding of complex biological systems such as the brain.
Clinical trials are observations or experiments done in clinical research. It includes biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants to answer specific questions about treatments such as novel vaccines, drugs, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices. It generates data on efficacy and safety. Clinical trials are conducted only after they receive approval from the ethics committee in the country. These authorities are responsible for benefit or risk ratio of trial and the approval does not mean the therapy is safe; it is that only the trial may be conducted. The cost of a trial is dependent on a number of factors. The sponsor for clinical trials may be a pharmaceutical company or government organization or medical device company. There are certain functions which are necessary to the trial include lab work and monitoring, managed by central laboratory or contract research organization.
Emergency medical services, known as ambulance services or paramedic services. These are emergency service for providing transport to definitive care, and other medical transport of patients with illness and injuries. Emergency medical services may also be locally known as ambulance corps, life squad, rescue squad, first aid squad. The main goal of most emergency medical services is to arrange for timely removal of the patient to the next point of definitive care, or provide treatment to those in need of urgent medical care. This is an emergency department at the hospital. Emergency medical service change from providing ambulances only for transport, to preliminary medical care which is given during transport. In some regions, the term is not used, or may be used inaccurately, because the service in question does not provide treatment to the patients, but only provides transport to the point of care.
Electronic Medical Record and Disease Management:
Electronic medical record refers to patient health information in a digital format. Records can be shared through enterprise-wide information systems or other information networks and exchanges. Electronic medical record includes range of data which includes medical history, laboratory test records, vital signs, billing information, radiology images. Electronic medical record systems are designed to store data accurately and to capture the state of a patient across time. Due to the digital information being searchable in a single file, electronic medical records are more effective when extracting medical data for the examination of possible trends and long term changes in a patient. Disease management is defined as health care interventions and communications for populations in which patient self-care efforts are significant.
Market Analysis
Population: 8.6 million GDP: $374.3 billion ($43,711 per capita)
Healthcare spending in Austria in 2014 was $47.9 billion. It includes both operating costs and investment, which adds up to 11% of GDP. Healthcare spending in Austria has been increasing at a rate of 5% annually over the past twenty years.
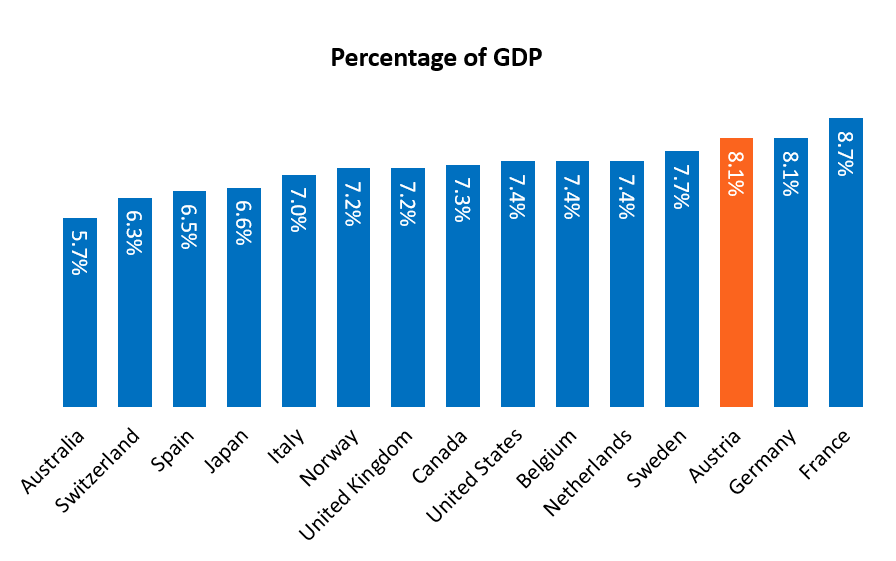
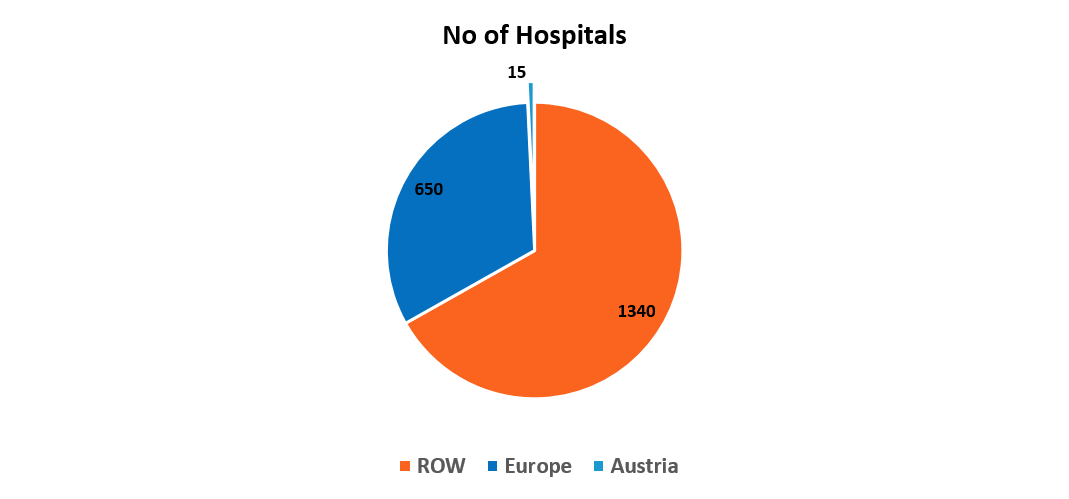
Austria has 275 hospitals and clinics with around 64,800 available beds (760 hospital beds/100.000 population, one of the highest in Western Europe). Around two-thirds of hospital beds are in general hospitals, 26% are in specialized clinics and rehabilitation centers, 7% are in sanatoriums and 5% in long-term care facilities. In 2014, there were 43,126 medical doctors practicing in Austria, or 502 doctors/100,000 population, and 2,243 registered pharmacies.
Austria has a single-payer national healthcare insurance program within their federal social insurance administration. This system covers almost 100% of the population (over 8.5 million insured) with unemployment, disability, pension and health insurance programs. Around 76% of non-investment healthcare costs are covered publicly. Capital investment, which makes up around 7% of total healthcare spending, is financed 60% publicly and 40% privately.
U.S. medical devices and pharmaceutical products have an excellent reputation and a strong market position in Austria. Best prospects are Health IT, as well as products and medications for an ageing population (dental consumables, screening and early diagnostic technologies, cardiovascular treatments, bone health, orthopedics, cancer treatments, dementia care,.) and various products/methods that help cut costs (minimally invasive surgical methods/products, preventive medicine, cheaper and more efficient screening and diagnostic technologies, etc.).
Current market trend:
There are three main drivers in Austria’s healthcare market: 1) the desire on the part of public healthcare payers to rein in spending without losing quality of care means that reducing waste and improving efficiency are increasingly important; 2) a high level of innovation in the sector, accompanied by increasing patient and physician awareness about options; and 3) an ageing population. In 2005, 16% of the population was over 65. In 2015, that number had risen to 18.5% and it is estimated that by 2030 24% of the population will be over 65.
Competitors:
Austria imports the lion’s share of its medical devices. Major players are Germany (around 33% of the market), the United States (15-20%), Switzerland, South Korea, the Netherlands, China and Japan.
In the pharmaceutical sector, Austrian firms compete on the generics market and are successful in the sale of natural and homeopathic remedies. Patented and innovative pharmaceuticals tend to be imported from the major multinational pharmaceutical companies. U.S. products have seen excellent success and are considered to be at the cutting edge of medical technology. The U.S. holds around 18% of the import market and the Austrian operations of U.S. companies (Baxter, Pfizer) are seen as local champions in the biotech sector.
Companies associated with internal medicine and patient care:
- KCI Austria
- SCHILLER
- C. R. Bard
- Richard Wolf
- West Medica production
- Lohmann & Rauscher
- Anton Paar
- TMA Medical
- SANOFI GENZYME
- Shire
- VIFOR PHARMA
Learn More
Top Internal Medicine Universities Worldwide:
Europe Internal Medicine Universities:
- Medical University of Vienna
- Medical University of Innsbruck
- Karl Landsteiner University of Health Sciences
- Johannes Kepler University Linz
- Medical University of Graz
- Paracelsus Private Medical University of Salzburg
- Medical University Pleven
- Medical University of Plovdiv
- Medical University of Sofia
- Medical University of Varna
- Medical School University of Cyprus
- Saint George's Medical School in Cyprus
- School of Medicine European University Cyprus
- Aalborg University
- Aarhus University
- University of Copenhagen Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences
- University of Southern Denmark
- Aix-Marseille University
- Albert Ludwig University of Freiburg
- Ruprecht Karl University of Heidelberg
- National University of Ireland, Galway
- University College Dublin
- Universiteit van Amsterdam
- University of Groningen
- Universiteit Maastricht
- I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University
- St. Petersburg State University
- University of Ljubljana
- University of Maribor
- University of Alcalá
- University of Barcelona
- European University of Madrid
- Euroscicon
- University of Oviedo
- University of Basel
- University of Berne
- Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry
- Brighton and Sussex Medical School
- Bristol Medical School
- Durham University School of Medicine and Health
- Hull York Medical School
- Imperial College School of Medicine
- Keele University School of Medicine
- King's College London School of Medicine and Dentistry
- Lancaster Medical School
- Euroscicon
- Leeds School of Medicine
- Leicester Medical School
- Liverpool Medical School
- Manchester Medical School
- Medical Sciences Division, University of Oxford
- Euroscicon
- Newcastle University Medical School
- Norwich Medical School at The University of East Anglia
- Peninsula College of Medicine and Dentistry
- St George's, University of London
- School of Clinical Medicine, University of Cambridge
- Sheffield Medical School
- Southampton Medical School
- UCL Medical School
- Euroscicon Conferences
- University of Birmingham Medical School
- University of Nottingham Medical School
- Warwick Medical School
USA Internal Medicine Universities:
- Georgetown University School of Medicine
- George Washington University Medical School
- University of Connecticut School of Medicine
- California Northstate University College of Medicine
- University of South Alabama College of Medicine
- University of Alabama School of Medicine
- Charles R. Drew University of Medicine and Science
- University of California, Irvine School of Medicine
- Euroscicon Conferences
- UCSF School of Medicine
- University of Colorado School of Medicine
- University of Central Florida College of Medicine
- University of South Florida College of Medicine
- Morehouse School of Medicine
- Michigan Medicine
- University of Virginia
- Northwestern University
- University of Rochester
- Euroscicon
- The University of Arizona Health Sciences
- University of Chicago
- Standford University
- Indiana University
- Southern Illinois University School of Medicine
- Duke University School of Medicine
- Harvard Medical School
- Johns Hopkins School of Medicine
- Emory University School of Medicine
- Yale School of Medicine
- Euroscicon Conferences
- Baylor College of Medicine
- Washington University School of Medicine
- Mayo Clinic College of Medicine
- Wayne State University School of Medicine
- University of Massachusetts Medical School
- University of Maryland School of Medicine
- Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
- University of Kansas School of Medicine
- Rush Medical College
- Euroscicon
- Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine
- Medical College of Georgiaat Augusta University
- Florida State University College of Medicine
- Howard University College of Medicine
Asia Internal Medicine Universities:
- Tra Vinh University
- Vietnam National University, Hanoi
- Vinh Medical University
- Aino University
- Baika Womens University
- Morinomiya University of Medical Sciences
- Kansai University
- Euroscicon Conferences
- Osaka University
- Kindai University
- Tokyo University
- Tambov State University
- Tver State Medical Academy
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences
- Army College of Medical Sciences
- University College of Medical Sciences
- Beijing University of Chinese Medicine
- Euroscicon
- Capital Medical University
- Peking Union Medical College
- Guangdong Medical University
- Hainan Medical College Harbin Medical University
- International University - Cambodia (IU)
- Euroscicon Conferences
- University of Health Sciences - Cambodia (UHS-C)
- University of Puthisastra (UP)
- Akaki Tsereteli State University
- David Agmashenebeli University of Georgia
- Tbilisi State Medical University
- Hashemite University
- Jordan University of Science and Technology
- Mutah University
- Euroscicon
- University of Jordan
- Nanyang Technological University
- National University of Singapore
- Mordovian Ogarev State University
- Moscow Medical Stomatology Institute
- Omsk State Medical Academy
Europe Internal Medicine Societies:
- Academy of Allergology Clinical Immunology
- Academy of Dermatology & Venereology
- Association of Senior Hospital Physicians
- Board of Cardiovascular Perfusion
- British Association of Dermatologists
- Drug Information Association
- Euroscicon
- European Association for Cardio-Thoracic
- European Association of Neurosurgical Societies
- European Association of Plastic Surgeons
- European Association of Radiology
- European Board for Accreditation in Cardiology
- European Data in Health Research Alliance
- European Dermatology Forum
- Euroscicon Conferences
- European Federation of Allergy
- European Federation of Salaried Doctors
- European Society for Medical Oncology
- European Society of Cardiology
- European Society of Clinical Microbiology
- The European Section and Board of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- European Association for the Study of the Liver
- World Gastroenterology Organization
- European Liver Patients Association
- Albanian Association of Gastroenterology & Hepatology
- Austrian Society of Gastroenterology & Hepatology
- Byelorussian Gastroenterology Association
- Royal Belgian Society of Gastroenterology
- Flemish Association for Gastroenterology (VVGE)
USA Internal Medicine Societies:
- American Association for Cancer Research
- American Board of Medical Specialties
- Aerospace Medical Association
- American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists
- American Board of Emergency Medicine
- American Board of Family Medicine
- American Board of Hospital Medicine
- American Board of Internal Medicine
- American Board of Legal Medicine
- American Board of Nuclear Medicine
- American Board of Ophthalmology
- Euroscicon
- American Board of Pain Medicine
- American Board of Pediatrics
- American Board of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- American Board of Physician Specialties
- American Board of Preventive Medicine
- Los Angeles County Medical Association
- Medical Association of Georgia
- Euroscicon Conferences
- American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD)
- North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition
- Gastroenterology & Hepatology Associates
- American College of gastroenterology
- American Gastroenterological Association
- American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Asia Internal Medicine Societies:
- Australasian College for Emergency Medicine
- Australian Medical Association
- Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists
- Doctors Reform Society of Australia
- National Prescribing Service
- Royal Australasian College of Physicians
- Euroscicon
- Royal Australasian College of Surgeons
- Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Radiologists
- Royal Australian College of General Practitioners
- Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists
- Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
- Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Ophthalmologists
- Euroscicon Conferences
- Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Radiologists
- Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia
- Indian Orthopaedic Association
- Ibn Sina Academy of Medieval Medicine and Sciences
- Indian Academy of Pediatrics
- Academy of Family Physicians of India
Europe Internal Medicine Conferences:
- 7th Edition of International Conference on Family Medicine & Primary Care Paris, France
- 9th Edition of International Conference on Alternative Medicine London, UK
- 2nd Edition of International Congress on Pediatrics Edinburgh, Scotland
- 8th Edition of International Conference on CASE REPORTS London, UK
- 8th Edition of International Conference on Hepatology Vienna, Austria
- 6th Edition of International Conference on Infectious Diseases London, UK
USA Internal Medicine Conferences:
- 5th International Conference on Pain Management and Pain Medicine New York, USA
- 16th Annual Dialysis & Renal Medicine Conference Baltimore, Maryland, USA
- International Conference on Applied Psychology and Behavioral Medicine Toronto, Ontario, Canada
- 30th International Conference & Exhibition on Dental Medicine & Dental Implants Atlanta, USA
- International Conference on Oncogenesis and Oncologic Emergency Medicine San Diego, USA
- 3rd International Conference on Internal Medicine and Hospital Medicine Toronto, Ontario, Canada
- 9th International Conference on Predictive, Preventive and Personalized Medicine & Molecular Diagnostics Boston, USA
Asia Pacific & Middle East Internal Medicine Conferences:
- International Conference on Internal Medicine Osaka, Japan
- 4th Global Summit on Herbals and Traditional Medicine Osaka, Japan
- 11th World Congress on Orthopedics, Rheumatology & Sports Medicine Sydney, Australia
- 11th World Congress on Rheumatology, Orthopedics & Sports Medicine Sydney, Australia
- 9th International Conference on Tissue Science and Regenerative Medicine Sydney, Australia
- 7th International Conference on Telemedicine & Medical Informatics Melbourne, Australia